Energy Consumption & CO2 Emission Report from Commercial Buses in India ( as per early 2025 available data)
GRAPH
For Energy Consumption :
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) buses consume an average of 2.8 kWh/km, leading to a massive total energy consumption (Total energy consumption : 2.8×56,384=157,875.2 kWh/km2.8×56,384=157,875.2 kWh/km) of
157,875.2 kWh/km across 56,384 ICE buses. = 156.8 MWh/Km c
In contrast, Electric Vehicle (EV) buses consume only 1.15 kWh/km, totaling (1.15×3,616=4,158.4 kWh/km) just 4,158.4 kWh/km for the 3,616 EV buses = 4.16 MWh/Km
Methods to illustrate :
energy consumption of ICE Bus = massive commercial airplane at an airport with fuel trucks loading it up
EV Bus = Smartphone plugged into a charger with a small battery icon.
For CO2 Emission:
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) buses emit an average of 1.5 kg of CO₂ per km, leading to a massive total CO₂ emission of:
Total CO₂ Emissions: 1.5×56,384=84,5761.5= 84,576 kg/km (across 56,384 ICE buses) = 84.58 Ton/Km
In contrast, Electric Vehicle (EV) buses have no tailpipe emissions, but when accounting for grid electricity, they emit around 0.9 kg of CO₂ per km, totaling.
Total CO₂ Emissions: 0.9×3,616=3,254.40.9 = 3,254.4 kg/km (across 3,616 EV buses) = 3.25 Ton/Km
Methods to Illustrate:
ICE Bus = A Giant Parachute Needing Massive Air
EV Bus = A Simple Balloon
Market Growth and Regional Distribution
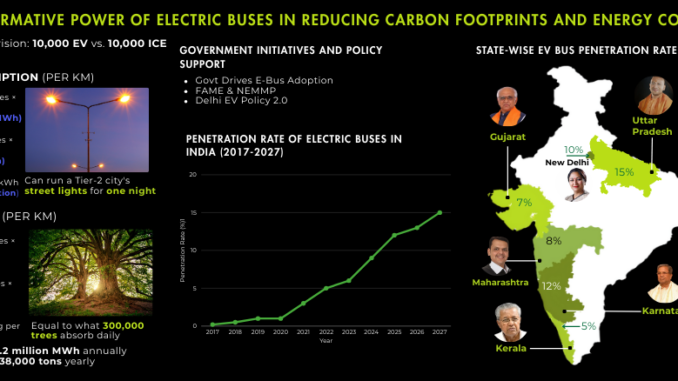
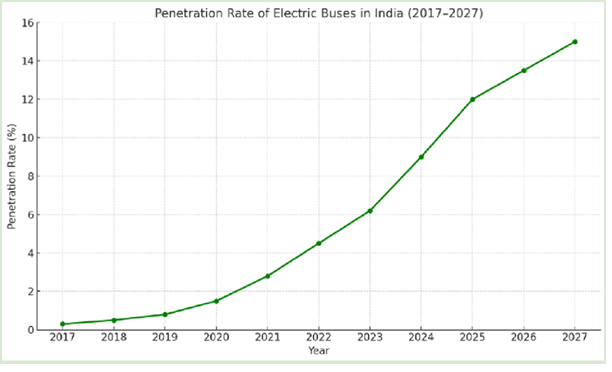
- The Indian e-bus market is growing rapidly, with sales projected to increase 3.6 times by FY27, reaching over 17,000 units, up from just 3,644 units in FY24. This indicates a strong upward adoption trend, backed by government policies and cost advantages.
- Despite currently comprising just 4% of annual bus registrations, e-buses experienced an impressive 81% year-on-year growth in FY24, showcasing increasing demand despite a relatively low base. By FY27, their penetration in the market is expected to reach 15%, significantly reshaping India’s public transport sector.
- India currently has only six e-buses per million people, a stark contrast to the global average of 85 per million, highlighting massive growth potential. Maharashtra leads e-bus adoption with 2,423 registrations, followed by Delhi (2,361) and Karnataka (1,473), demonstrating strong regional uptake in urban centers.
Industry Leaders and Manufacturing Capacity
- The Indian e-bus industry is highly concentrated, with five major manufacturers holding 88% market share in FY24. This includes Tata Motors, Olectra Greentech, JBM, PMI, and Switch Mobility.
- Tata Motors dominates the sector, with 1,431 registrations in 2024, accounting for 40% of the heavy passenger electric vehicle market. The company’s strong production capacity and supply chain advantage have cemented its leadership position.
- These five key players collectively have an annual production capacity of 40,500 e-buses, demonstrating India’s readiness for large-scale adoption and the ability to support rapid expansion in the coming years.
Economic Advantages and Operational Benefits
- The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for air-conditioned electric buses is estimated to be 15-20% lower than that of equivalent diesel buses over a 12-year operational period. This makes EV buses an economically viable long-term investment despite higher initial purchase costs.
- The Gross Cost Contract (GCC) model is emerging as the preferred operational structure, reducing financial burden on State Transport Undertakings (STUs) by shifting operational and maintenance responsibilities to private operators. This asset-light approach is particularly beneficial for urban transport agencies in large cities.
- The per-kilometer operating cost of electric buses is significantly lower than diesel buses, leading to long-term operational savings. With continued advancements in battery technology and declining battery costs, these savings are expected to further improve over time, making e-buses even more financially attractive.
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
- The PM e-Bus Sewa Scheme is a flagship government initiative, allocating $2.4 billion to support the deployment of 10,000 electric buses across 169 cities. The scheme follows a public-private partnership (PPP) model, ensuring cost-effective deployment and operation, with full implementation expected by 2026.
- Additional incentives are provided under the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme and the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP), which focus on charging infrastructure expansion, direct subsidies, and R&D support for EV technology.
- Delhi’s EV Policy 2.0 is one of the most ambitious state-level initiatives, targeting 95% of new vehicle registrations to be electric by 2027. The policy also mandates a complete transition of Delhi’s bus fleet to EVs, backed by state EV funds, green levies, and pollution cess revenues. To support this shift, the government is expanding fast-charging corridors along major routes like the Ring Road and Outer Ring Road, ensuring smooth operational feasibility for e-buses.
Electric bus (e-bus) adoption in India has gained significant momentum over the past few years, driven by government incentives, climate commitments, and the need to modernize public transportation. The push for greener mobility solutions has led various Indian states to incorporate e-buses into their fleets at varying scales. Programs like the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME II) scheme have been central in this transition, with over 5,000 e-buses sanctioned for deployment across cities.
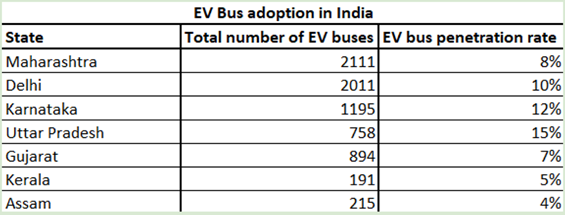
Among the frontrunners, Maharashtra leads in terms of the absolute number of electric buses, with over 2,100 units in operation. This is followed closely by Delhi, which not only has over 2,000 e-buses but also boasts one of the highest penetration rates at around 10%. Delhi’s aggressive electrification policies and strong political commitment to reduce air pollution have contributed to its rapid adoption. Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh also show promising trends. Karnataka, with around 1,200 e-buses, has a penetration rate of approximately 12%, while Uttar Pradesh, though with fewer buses (around 758), leads in terms of penetration, with 15% of its public fleet being electric.
Other states like Gujarat, Kerala, and Assam have also entered the race, albeit with smaller fleets. Gujarat has nearly 900 e-buses, while Kerala and Assam operate over 190 and 215 e-buses respectively. These states are in the early stages of scaling their electric fleets and are supported by both central government funding and state-level policies focused on clean energy transitions.
Despite the progress, challenges remain in terms of charging infrastructure, high initial procurement costs, and operational readiness, particularly in smaller cities. Nonetheless, the overall trajectory indicates that India is steadily moving toward its goal of a cleaner and more sustainable public transport system. As more states ramp up adoption and infrastructure improves, the share of electric buses in India’s urban transport networks is expected to rise significantly by 2030.
References
https://emobilityplus.com/2024/07/26/cesl-and-niti-aayog-drive-forward-with-over-11000-electric-buses-deployed-across-india/
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2043645 (FAME II specific only)
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/india-e-bus-industry-report-145500770.html
https://www.autocarpro.in/news/indias-electric-bus-market-soars-81-poised-for-15-share-by2027-125352
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1386180/india-electric-bus-penetration-rate
https://www.business-standard.com/industry/auto/india-s-e-bus-sales-likely-to-grow-3-6-foldin-fy27-projects-careedge-125031100837_1.html
https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/12/10/2994451/28124/en/India-ElectricBus-Market-Report-2024-Featuring-Profiles-of-JBM-Auto-Olectra-Greentech-Solaris-Bus-Coach-PMI-Electro-Mobility-Solutions-Switch-Mobility-Tata-Motors-GreenCell-Mobili.html
https://www.imarcgroup.com/india-electric-bus-market


